Going Mobile First Reduces Costs, Increases Capabilities For Public Safety Agencies
January 8, 2021
Your Network is Only as Reliable as its Power Infrastructure
January 8, 2021The Transition to Mobile First
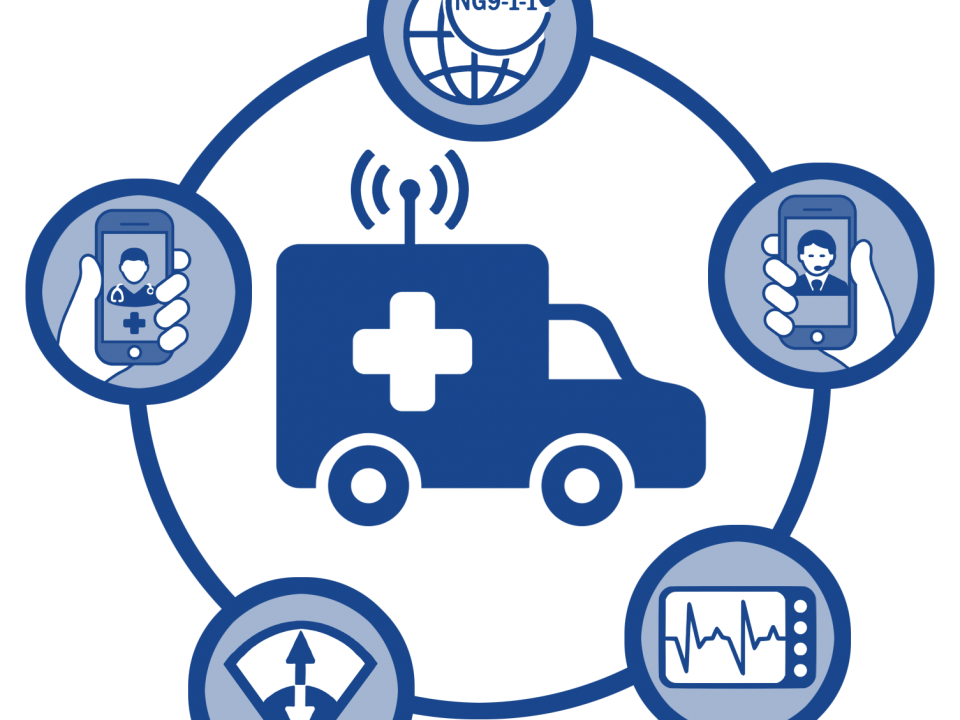
In the past, public safety has relied on expensive, capital intensive, private radio systems, such as TETRA, TETRAPOL and P25 for mission-critical voice communications. While these technologies have provided reliable narrowband communications, they have inherently limited the ability of public safety to leverage more modern broadband technologies. In addition, agencies have had to incur large capital expenditures in the millions and tens of millions of dollars to implement such capabilities, which have put significant pressure on agency budgets. As available federal grant programs continue to dwindle, more and more financial pressure on these agencies will come to bear.
During this same time, wireless broadband technologies, which due to the ubiquitous and commercial nature of such networks are significantly less capital intensive for public safety purchasers, have advanced significantly, particularly with the deployment of long-term evolution (LTE) cellular services, and the planned roll out of 5G. However, historically these networks were not architected specifically to provide reliable mission critical communication capabilities public safety needs.
However, the advent of public safety-focused LTE networks has now solved this problem by prioritizing public safety traffic over all other traffic, ensuring that public safety is always able to communicate without delay or impediment. These broadband networks also incorporate enhanced security and offer dedicated public safety applications designed for the needs of public safety. These will include, for example, mission-critical push-to-talk and peer-to-peer capabilities, situational awareness and mapping capabilities, and secured cloud-based communications platforms and records management, as well as new predictive analytics tools. These network upgrades have significantly changed the public safety communications landscape enabling public safety for the first time to really leverage wireless cellular broadband networks for their mission-critical communications.
- the ability to scale user subscriptions based on need
- the distribution of costs on a monthly basis, resulting in more stable cash flows;
- significant reduction in capital maintenance and upgrade costs, which are included in the monthly service fees;
- built-in innovation and upgrades to software and technology without additional costs